Conservation procedures
The preservation of the original features of conserved yeasts is the mission of the DBVPG Collection.
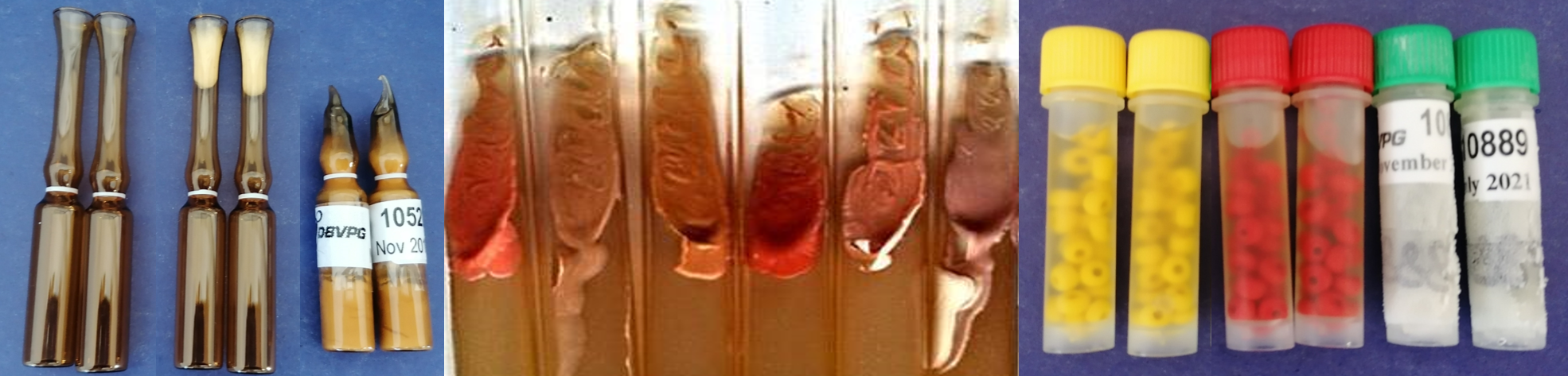
Accordingly, preservation on agar has been abandoned by favouring long-term storage realized in two ways: (i) conservation in the form of freeze-dried cultures maintained at 5°C, (ii) cryopreservation at -80°C.
Periodically, cultures are randomly chosen and tested for viability and characters stability.
Yeast cultures conserved in each of the two forms mentioned are maintained in separate sectors of the Department of Agricultural, Food and Environmental Sciences and the refrigeration systems are under the control of specific automatic alarms that allow immediate detection of anomalous conditions remotely, in order to reduce the risk of accidental leaks, in accordance with the Budapest Treaty on the conservation of biological resources.
Nomenclature of conserved cultures
Species names of the conserved cultures are updated accordingly to (i) the ca. 1,500 specie described in the 5th edition of the monograph: “The Yeasts. A Taxonomy Study”, Kurtzman C.P., Fell J.W. & Boekhout T. (eds.) Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2011, (ii) The Yeasts Trust that, via its website (https://theyeasts.org/) provides the most up-to-date and complete taxonomic information on all published yeasts, and (iii) the current literature published in more recent months.
However, since the nomenclature of yeasts is constantly evolving, in order to facilitate the use of the database even by those not updated with respect to the latest taxonomic information, the obsolete names of some species have not been completely eliminated but have been reported among the synonyms, to allow a search also based on the old taxonomy.
The most common synonyms and the name of the asexual state (anamorph) are also included in correspondence with the names under which the different yeast strains have been classified.